

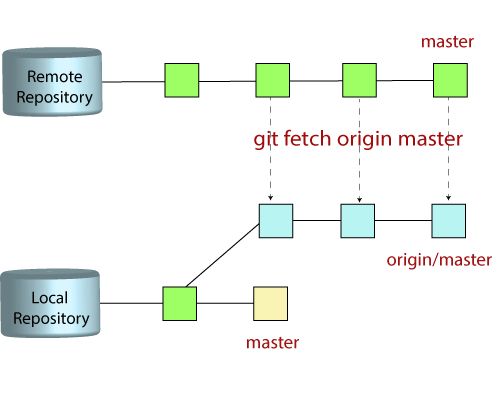
This branch will have the final, up-to-date, production-ready code.When a new Git repository is initialized using the Git Init command, it will only have a single branch and that branch, by default, is called the master.Master is the default name that Git gives to a branch when we create a new repository.We can also change this default name with the help of the Git Remote Rename command. We can see in the image below that we have a remote called origin. Next, we are going to check the remotes present by using the Git Remote command. First, we will run the Git Clone command, and pass the URL for the remote repository. There is nothing extraordinary about this word and we can use any other name that we like.Ĭonsider the example below where we try to clone a remote repository to our local system. It is a standard default name given to the repository from where our local repository originated.This name will be used in the future when we have to push or pull changes from the remote repository. In Git terminology, the origin is the name given to the remote repository from where we clone our local repository. This same definition can be applied to the word origin which is used in Git.

Origin, in simple terms, is described as the place from where something begins or is derived.Let's learn more about origin and master, and see how they are used. Origin is the default name given to a remote repository, and master is simply a branch name. Origin and master are two terms frequently used when working on a project managed using Git.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
